ASSESSMENT OF GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS
Views: 263
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the main cause of anthropogenic climate change. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the most common greenhouse gas. Other greenhouse gases include methane, nitrous oxide and other gases that trap heat and cause warming. Different greenhouse gases have different abilities to trap heat in the atmosphere, so greenhouse gases are quantified as carbon dioxide equivalents (CO2e).
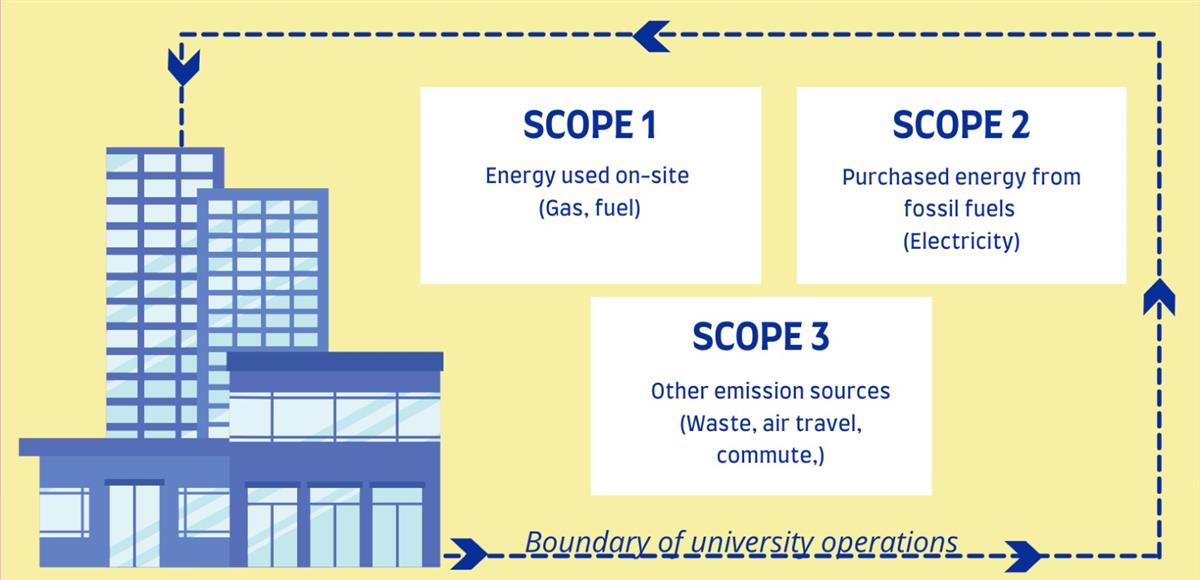
The Greenhouse Gas Protocol (https://ghgprotocol.org/standards) classifies an organization's greenhouse gas emissions into three tracking and reporting categories:
- Scope 1 – All direct emissions from the activities of the organization or under its control. Including combustion of fuel on site, for example in gas boilers and vehicles.
- Scope 2 – Indirect emissions from electricity purchased and used by the organization. Emissions occur during energy production and are ultimately used by the organization.
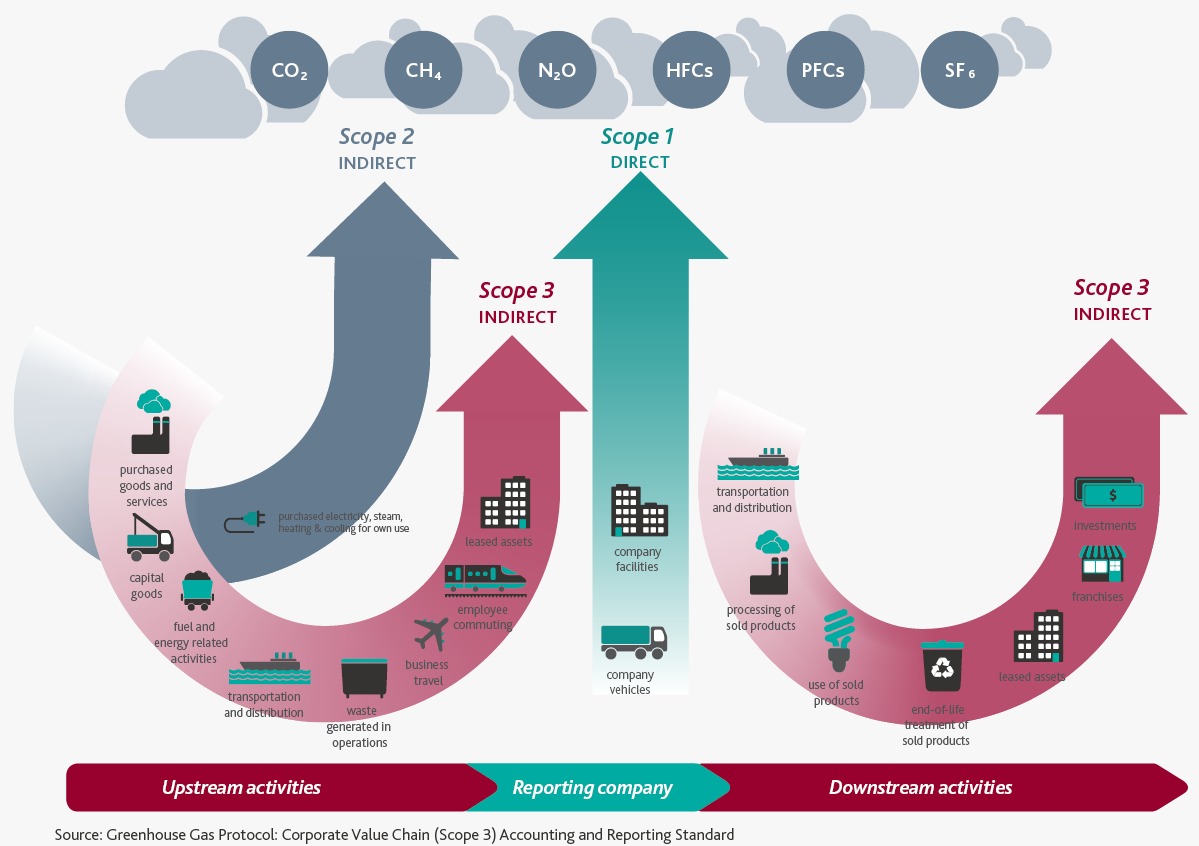
- Scope 3 – All other indirect emissions from an organization's activities that originate from sources that it does not own or control. They typically account for the largest share of the carbon footprint, covering emissions associated with business travel, purchasing, waste and water.
Scope 3 covers all indirect GHG emissions that were not included in Scope 1 and 2. Scope 3 GHG emissions are currently not subject to mandatory reporting under the GHG Protocol, which only considers direct emissions from stationary combustion, flaring, as well as fuel combustion in transport and emissions from technological processes and waste.
As a result of the activities of Al-Farabi Kazakh National University, there are emissions that are not owned or controlled by the University, classified as category 3 emissions.
Scope 3 emissions coverage includes:
• purchased goods and services
• capital goods
• fuel and energy activities
• transportation and distribution
• waste generated during operation
• business trip
• processing of sold products
• use of sold products
• processing of sold products at the end of their service life
• attachments.
One of the goals of the University's Sustainability Plan and 2035 Carbon Neutrality Strategy is to account for and reduce Scope 3 emissions. The University is conducting an analysis of Scope 3 emissions, looking at the different categories that we can track. We have identified the following areas of relevance to the activities of the university:
• waste generated during operation;
• number of transport trips on campus;
• indirect emissions typical for educational institutions.
Most of these categories began tracking in 2016.
SCORE 3 GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS CALCULATION
a. Electricity usage per year (EC 2.7)
The CO₂ emission from electricity
= (electricity usage per year in kWh/1000) x 0.84
= (9 660 kWh/1000) x 0.84
= 8. 1144 metric tons
Notes:
Electricity usage per year= 9 660 kWh
0.84 is the coefficient to convert kWh to metric tons
b. Transportation per year (Shuttle) (TR 5.6)
= (Number of the shuttle bus in university x total trips for shuttle bus service each day x approximate travel distance of a vehicle each day inside campus only (in kilometers) x 240/100) x 0.01
= ((2 x 4 x 4 x 240)/100)) x 0.01
= 0.768 metric tons
Notes:
240 is the number of working days per year
0.01 is the coefficient to calculate the emission in metric tons per 100 km for bus
c. Transportation per year (Car) (TR 5.2)
= (Number of cars entering university x 2 x approximate travel distance of a vehicle each day inside campus only (in kilometers) x 240/100) x 0.02
= ((240 x 2 x 4 x 240)/100)) x 0.02
= 92.16 metric tons
Notes:
240 is the number of working days per year
0.02 isthe coefficient to calculate the emission in metric tons per 100 km car
d. Transportation per year (Motorcycle) (TR 5.3)
= (Number of motorcycle entering university x 2 x approximate travel distance of a vehicle each day
inside campus only (in kilometers) x 240/100) x 0.01
= ((0 x 4 x 4 x 240)/100)) x 0.01
= 0 metric tons
Notes:
240 is the number of working days per year
0.01 is the coefficient to calculate the emission in metric tons per 100 km for motorcycle
e. Total emission per year
= total emission from electricity usage + transportation (bus, car, motorcycle)
= 8. 1144 + (0.768 + 92.16 + 0)
= 101. 0424 metric tons








